Practical No: 1
Title: Perform the practical
on my network places.
Aim: To learn how to work with my network places.
Description:
My Network Places replaces
Network Neighborhood in Windows for browsing available network connections,
computer, and devices. In a home network setting, My Network Places can display
the other computers, network printers, and other network resources. In an
office setting, it can display computers, servers, and network printers in the
users local workgroup. With the release of Microsoft Windows Vista and Windows
7, My Network Places is renamed to Network.
To gain access to the Windows
7 Network and Internet.
Follow the following steps:
1.
Click on start
button click on control panel. Control panel window will get appeared.
2.
Choose category
option.
3.
Select and click
on network and internet
4.
Click on network
and sharing center
5.
It will show you
the available and currently active network connections.
If there is no any available
connection then there is a need to setup a new connection or network for that
you have to follow the following steps:
1.
Click on setup a
new connection or network it will open a
new interface through which you can;
a.
Connect to the
internet
b.
Setup a new
network
c.
Manually connect
to a wireless network
d.
Connect to
workplace
e.
Setup a new
dial-up connection
Choose an option from the above
and configure as per the interface or wizard.
Practical No: 2
Title: Study the OSI
reference model.
Aim: To understand the layers of OSI reference
model.
Description:
Write this practical from
Notes provided to you.
Practical No: 3
Title: Study the TCP/IP model.
Aim: To understand the layers of TCP/IP model.
Description:
Write this practical from
Notes provided to you.
Practical No: 4
Title: Perform practical on
creating user.
Aim: To understand how to create users in windows
OS.
Description:
Set Up a New Account with
Standard Privileges
1. From the Start menu, choose computer, and then right click
and select Manage.
2. Click on Select system tools then click on local users and
groups.
3. Then Select users.
4. Right click on right plane. And select New user from pop-up
menu.
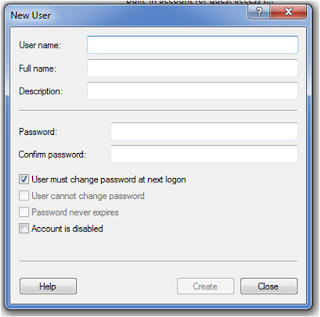
5. Then a new user creation window will appear.
6. Fill the user name along with other details
and uncheck the first option i.e. user must change passward at next logon.
7. Then check user cannt change passward and
passward never expires.
8. And finally click on create button.
Practical No: 5
Title: Perform the practical
on creating groups.
Aim: To understand how to create user groups in
windows OS.
Description:
You can manage your groups and users in Windows by creating a new group and user. Upon creating, you will then be able to add them into either Trusted Groups or Trusted Users so that they can be listed as Trusted Accounts who have the rights to modify the whitelist.
Follow these steps to create new groups and users in Windows:
Create a new group in Windows
1. Go to Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Computer Management
2. Navigate to Local Users and Groups under Computer Management on the left panel. Click on Groups.
3. Right-click on the middle panel and click on New Group… when the right-click menu appears.
4. The New Group creation window will appear. Enter the group details and click the Create button.
5. The window will be cleared once the group is being created successfully. Repeat the previous steps to create more groups or else click the Close button to exit the New Group creation window.
6. The newly created group will appear under the Groups list.
Practical No: 6
Title: practical on LAN
sharing printer, files and folder over the network.
Aim: To understand LAN sharing printer, files and
folder over the network.
Description:
Step 1: Connecting the network hardware and cables to set up a local network
Do the following to set up the network hardware and connect the networking cables.
Set up and turn on the power for the network hub or other networking device.
Connect the computers to the networking device. If a crossover cable is used, connect the cable to the RJ45 network ports on each computer.
Connect the computer power cords and turn the computers on.
Step 2: Turning on Network discovery and file sharing in Windows 7
Turn on Network discovery and file sharing on each computer that you want to access on the network. Follow these steps to begin setting up the network:
Click Start , and then click Control Panel.
Under Network and Internet, click Choose Homegroup and sharing options.
Network and Internet section of Control Panel
In the Homegroup settings window, click Change advanced sharing settings.
Step 1: Connecting the network hardware and cables to set up a local network
Do the following to set up the network hardware and connect the networking cables.
Set up and turn on the power for the network hub or other networking device. (Follow the instructions provided by the manufacturer).
Connect the computers to the networking device. If a crossover cable is used, connect the cable to the RJ45 network ports on each computer.
Connect the computer power cords and turn the computers on.
Step 2: Turning on Network discovery and file sharing in Windows 7
Turn on Network discovery and file sharing on each computer that you want to access on the network. Follow these steps to begin setting up the network:
Click Start , and then click Control Panel.
Under Network and Internet, click Choose Homegroup and sharing options.
Network and Internet section of Control Panel
In the Homegroup settings window, click Change advanced sharing settings.
Homegroup settings window
Turn on network discovery and file and printer sharing. Review the other settings and turn them on or off.
Advanced sharing settings
Click Save changes.
Step 3: Sharing drives, folders, and files in a Windows 7 network
To share non-public folders with other computers on a local network, follow these steps:
Click Start , and then click Computer.
Browse to the folder you want to share.
Right-click the folder, select Share with, and then click Homegroup (Read), Homegroup (Read/Write), or Specific people.
Image of Share with menu options
If you chose Specific people, the File Sharing window displays.
Click the down arrow and select the account you want to share with, and then click Add.
NOTE: A User Account Control might open. You must accept this Window to make the necessary changes.
File Sharing window
Click an arrow under Permission Level to set the permission level for each account or group.
Click Share.
Step 4: Testing a local network in Windows 7
Open the Windows 7 network window and browse through the shared folders in each computer on the network. If the computer is able to read and access files from a remote computer, the remote computer is set up correctly. Browse to every available computer from each computer on the network. If there are any issues, go back through these steps and verify that the settings are correct.
For more information, refer to the section Accessing shared files and directories in Windows 7.
When all computers are able to network to each other on the network, continue with the next step to enable Internet access and the firewall.
Step 5: Enabling Internet access and firewall for a local network
Once you have verified that your home network is capable of transferring files, connect and enable Internet connections for computers with Internet access.
Accessing shared files and directories in Windows 7
Do the following to access shared files and directories in a local network:
Ensure network discovery and file sharing is turned On.
Click Start , click Control Panel, click Network and Internet, and then click Network and Sharing Center.
Double-click Network.
Network and Sharing Center
The Network window opens and displays computers with shared folders that are detected on local networks.
Network window
Double-click the computer you want to access.
NOTE: When accessing shared files or directories the following error message window may display: Figure : Cannot access PC Windows cannot access PC This error can be caused by the following:
Password Protection is On and the Guest account is On.
The account does not have permission to access the share. This typically occurs when specific permissions are set up on systems with multiple share folders.
NOTE: Windows 7 file sharing displays all the shared folders, even those you do not have permission to access.
To resolve the error, verify the following:
The account has the proper permissions to access the computer.
The computer name and account name are spelled correctly.
Make sure that Firewall software on any connected computer is set to allow access.
Homegroup settings window
Turn on network discovery and file and printer sharing. Review the other settings and turn them on or off.
Advanced sharing settings
Click Save changes.
Step 3: Sharing drives, folders, and files in a Windows 7 network
To share non-public folders with other computers on a local network, follow these steps:
Click Start , and then click Computer.
Browse to the folder you want to share.
Right-click the folder, select Share with, and then click Homegroup (Read), Homegroup (Read/Write), or Specific people.
Image of Share with menu options
If you chose Specific people, the File Sharing window displays.
Click the down arrow and select the account you want to share with, and then click Add.
NOTE: A User Account Control might open. You must accept this Window to make the necessary changes.
File Sharing window
Click an arrow under Permission Level to set the permission level for each account or group.
Click Share.
Step 4: Testing a local network in Windows 7
Open the Windows 7 network window and browse through the shared folders in each computer on the network. If the computer is able to read and access files from a remote computer, the remote computer is set up correctly. Browse to every available computer from each computer on the network. If there are any issues, go back through these steps and verify that the settings are correct.
For more information, refer to the section Accessing shared files and directories in Windows 7.
When all computers are able to network to each other on the network, continue with the next step to enable Internet access and the firewall.
Step 5: Enabling Internet access and firewall for a local network
Once you have verified that your home network is capable of transferring files, connect and enable Internet connections for computers with Internet access.
Accessing shared files and directories in Windows 7
Do the following to access shared files and directories in a local network:
Ensure network discovery and file sharing is turned On.
Click Start , click Control Panel, click Network and Internet, and then click Network and Sharing Center.
Double-click Network.
Network and Sharing Center
The Network window opens and displays computers with shared folders that are detected on local networks.
Network window
Double-click the computer you want to access.
NOTE: When accessing shared files or directories the following error message window may display: Figure : Cannot access PC Windows cannot access PC This error can be caused by the following:
Password Protection is On and the Guest account is On.
The account does not have permission to access the share. This typically occurs when specific permissions are set up on systems with multiple share folders.
NOTE: Windows 7 file sharing displays all the shared folders, even those you do not have permission to access.
To resolve the error, verify the following:
The account has the proper permissions to access the computer.
The computer name and account name are spelled correctly.
Make sure that Firewall software on any connected computer
is set to allow access.
Practical No: 7
Title: Perform the practical
on IP Config command.
Aim: To understand IP Config command.
Description:
Configure IP (internet protocol configuration)
|
IPCONFIG /all |
Display full configuration information. |
|
IPCONFIG /release [adapter] |
Release the IP address for the specified adapter. |
|
IPCONFIG /renew [adapter] |
Renew the IP address for the specified adapter. |
|
IPCONFIG /flushdns |
Purge the DNS Resolver cache. |
|
IPCONFIG /registerdns |
Refresh all DHCP leases and re-register DNS names. |
|
IPCONFIG /displaydns |
Display the contents of the DNS Resolver Cache. |
|
IPCONFIG /showclassid |
adapter Display all the DHCP class IDs allowed for adapter. |
|
IPCONFIG /setclassid adapter [classid] |
Modify the dhcp class id. |
If the Adapter name contains spaces, use quotes: "Adapter Name" wildcard characters * and ? allowed, see the examples below The default is to display only the IP address, subnet mask and default gateway for each adapter bound to TCP/IP. For Release and Renew, if no adapter name is specified, then the IP address leases for all adapters bound to TCP/IP will be released or renewed. For Setclassid, if no ClassId is specified, then the ClassId is removed.
Examples:
> ipconfig ... Show information.
> ipconfig /all ... Show detailed information
> ipconfig /renew ... renew all adapters
> ipconfig /renew EL* ... renew any connection that has its name starting with EL
> ipconfig /release *Con* ... release all matching connections, eg. "Local Area Connection 1" or "Local Area Connection 2"
> ipconfig /setclassid "Local Area Connection" TEST ... set the DHCP class ID for the named adapter to = TEST
Practical No: 8
Title: Perform the practical
on net view command.
Aim: To understand net view command.
Description:
The NET Command is used to manage File Shares, Printer Shares
and sessions.
Syntax:
NET VIEW
[\\computername [/CACHE] | [/ALL] | /DOMAIN[:domainname]]
Key:
/ALL Display
all the shares including the $ shares.
/CACHE Display
the offline client cache settings for resources on the specified computer.
computername A
computer whose shared resources you want to view.
domainname The
domain to view, by default all domains in the LAN.
Net View / ALL allows you to enumerate all the shares on a
remote computer, similar to the old ShareUI utility.
Examples:
Display a list of computers in the current domain:
NET VIEW
List the File/Printer shares on a remote computer:
NET VIEW \\ComputerName
NET VIEW \\127.0.0.1
List the shares on a remote computer including hidden shares:
NET VIEW \\ComputerName /All
List all the shares in the domain:
NET VIEW /DOMAIN
To see a list of shares on a different domain:
NET VIEW /DOMAIN:domainname
Practical No: 9
Title: Perform the practical on netstat command.
Aim: To understand netstat command.
Description:
Netstat — derived from the
words network and statistics — is a program that’s controlled via commands
issued in the command line. It delivers basic statistics on all network
activities and informs users on which portsand addresses the corresponding
connections (TCP, UDP) are running and which ports are open for tasks.
netstat commands for Windows
|
[OPTION] |
Command |
Description |
|
|
netstat |
Standard listing of all
active connections |
|
-a |
netstat –a |
Displays all active ports |
|
-b |
netstat –b |
Displays the executable file
of a connection or listening port (requires administrator rights) |
|
-e |
netstat -e |
Shows statistics about your
network connection (received and sent data packets, etc.) |
|
-f |
netstat-f |
Displays the fully qualified
domain name (FQDN) of remote addresses |
|
I |
netstat-i |
Brings up the netstat
overview menu |
|
-n |
netstat -n |
Numerical display of
addresses and port numbers |
|
-o |
netstat –o |
Displays the process
identifier (PID) associated with each displayed connection |
|
-p protokoll |
netstat –p TCP |
Displays the connections for
the specified protocol, in this case TCP
(also possible: UDP, TCPv6, or UDPv6) |
|
-q |
netstat -q |
Lists all connections, all
listening TCP ports, and all open TCP ports that are not listening |
|
-r |
netstat –r |
Displays the IP routing table |
|
-s |
netstat-s |
Retrieves statistics about
the important network protocols such as TCP, IP, or UDP |
|
-t |
netstat -t |
Shows the download status
(TCP download to relieve the main processor) of active connections |
|
-x |
netstat-x |
Informs about all
connections, listeners, and shared endpoints for NetworkDirect |
|
-y |
netstat-y |
Displays which connection
templates were used for the active TCP connections |
netstat -y
Netstat examples:
In order to make the use of the
listed netstat commands for Windows easier to understand, we will show you some
example commands:
List of all connections for the
IPv4 protocol
If you don't want to retrieve
all active connections, but only all active IPv4 connections, you can do this
using the netstat command:
netstat -p IP
Accessing statistics using the
ICMPv6 protocol
If you only want to obtain
statistics on the ICMPv6 protocol, enter the following command in the command
line:
netstat -s -p icmpv6
Practical No: 10
Title: Perform the practical on net user command.
Aim: To understand net user command.
Description:
Net user is a command-line tool
that is built into Windows Vista. To run net user, open a command prompt, type
net user with the appropriate parameters, and then press ENTER.
Syntax:
net user [<UserName>
{<Password> | *} [<Options>]] [/domain]
net user [<UserName>
{<Password> | *} /add [<Options>] [/domain]]
net user [<UserName>
[/delete] [/domain]]
|
Parameter |
Description |
|
<UserName> |
Specifies the name of
the user account to add, delete, modify, or view. The name of the user
account can have as many as 20 characters. |
|
<Password> |
Assigns or changes a
password for the user's account. Type an asterisk (*) to produce a prompt for
the password. The password is not displayed when the user types it at the
password prompt. |
|
/domain |
Performs the operation
on the domain controller in the computer's primary domain. |
|
<Options> |
Specifies a
command-line option. Refer to the next table for descriptions of the
command-line option syntax. |
|
net help
<Command> |
Displays help for the
specified net command. |
Examples:
The following example
displays a list of all user accounts for the local computer:
net user
The following example
displays information about the user account tommyh:
net user tommyh
No comments:
Post a Comment